You can do this using Windows’ built-in network resetting tool, found in the Windows Settings menu. This will reset your network devices, as well as other important components required for network connectivity, such as your TCP/IP stack. You can also change or reset network settings using the Windows PowerShell.
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Networking Issues
Before you reset network settings for your WiFi or wired ethernet devices, you may find that using the built-in Windows Troubleshooter can resolve common networking issues instead. This can often be a less drastic method for solving issues with your current network settings. A common issue, for instance, is an unavailable DNS server preventing websites from loading. The troubleshooting tool will check for problems like this and, if possible, resolve them automatically or help you resolve them yourself.
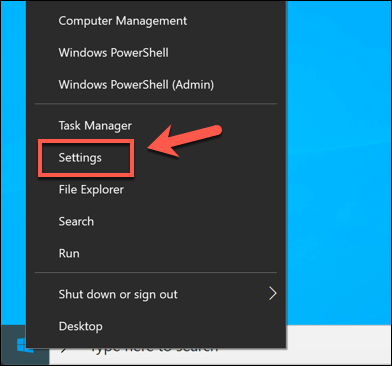
To use the Windows Troubleshooter, you’ll need to open the Windows Settings menu. To do this, right-click the Windows Start menu and press the Settings option.
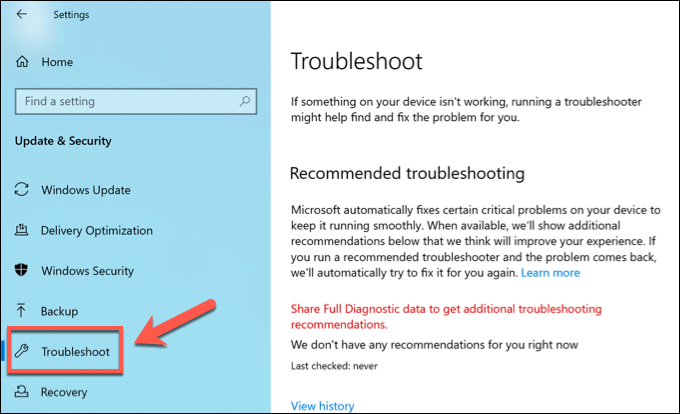
In the Windows Settings menu, press Update & Security > Troubleshoot. This will bring you to the Windows Troubleshooter.
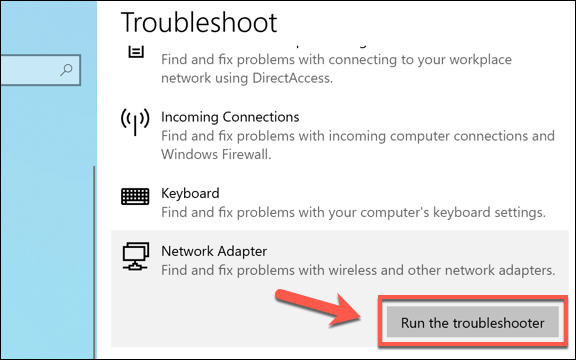
Several troubleshooting tools are available for your network connections. For instance, if your internet connection has issues, press the Internet Connections option in the Troubleshoot menu. If you’re struggling to connect to other local devices, press Incoming Connections. To troubleshoot your WiFi and ethernet adapters generally, press Network Adapters instead.
Press Run the Troubleshooter. This will load the troubleshooting tool, which will begin checking your adapters and active connections for issues.
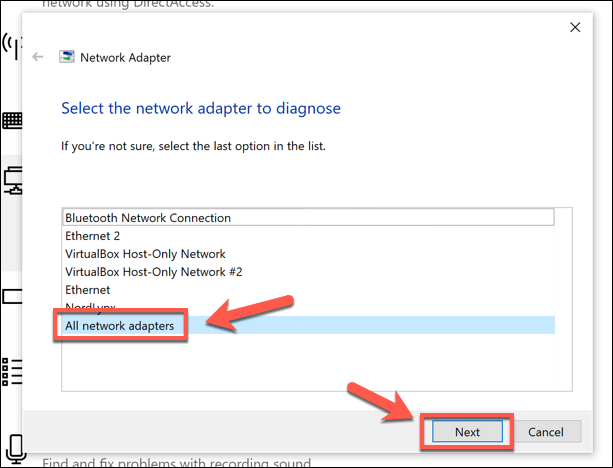
In the Troubleshoot window, Windows will begin scanning your devices and network configuration. If you selected Network Adapters, you’ll need to choose which adapter you wish to check, or press All network adapters to check all of your devices at once. Click Next to continue.
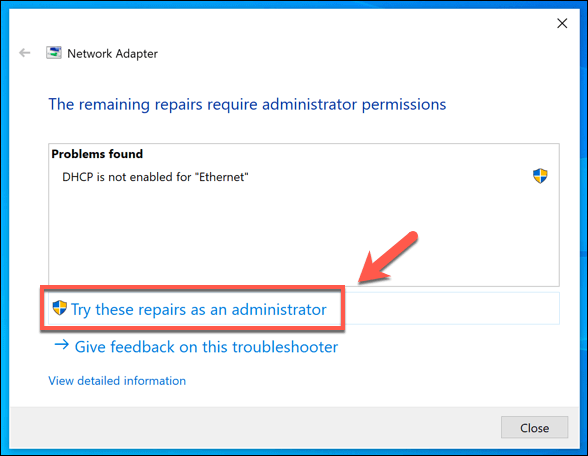
This will begin the troubleshooting tool, so wait a few moments for Windows to fully test your adapters, connections, and network configuration. If it detects any issues, these will be presented at the end for you to fix or will be fixed automatically. Click the Try these repairs as administrator option if you’re presented with a fix that Windows can perform automatically.
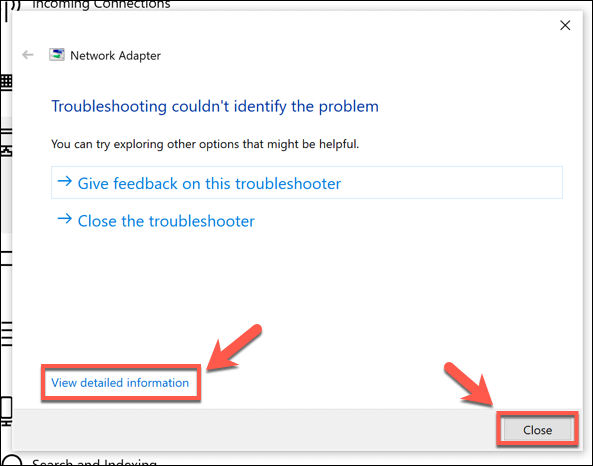
If the troubleshooter can’t detect any issues, it’ll inform you at the end that it couldn’t resolve the problem. Press the View detailed information button to view the full test report to help you identify an issue yourself, or press Close to close the tool.
While the Windows Troubleshooter can fix common issues with your network devices, it isn’t a miracle cure for potential settings conflicts or broken connections. If you’re still having issues, you’ll need to learn how to reset network settings in Windows 10 by following the steps below.
Using Windows Settings to Reset Network Settings in Windows 10
Like the Windows Troubleshooter, Microsoft includes a do-it-yourself tool for resetting your network settings in the Windows Settings menu. This will reset your network adapters and other network settings and protocols like your TCP/IP stack, which is essential for allowing your PC to make connections with other devices. If you’ve made any changes to your network configuration, you’ll need to restore these after you reset your devices. Before you do this, however, you should make sure that the changes you’ve made aren’t the cause of any network issues or conflicts to begin with, such as an IP address conflict on your network.
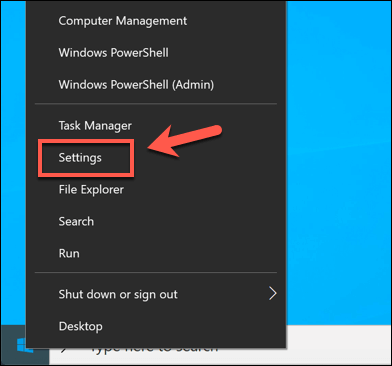
To reset network settings in Windows 10, right-click the Start menu and press the Settings option.
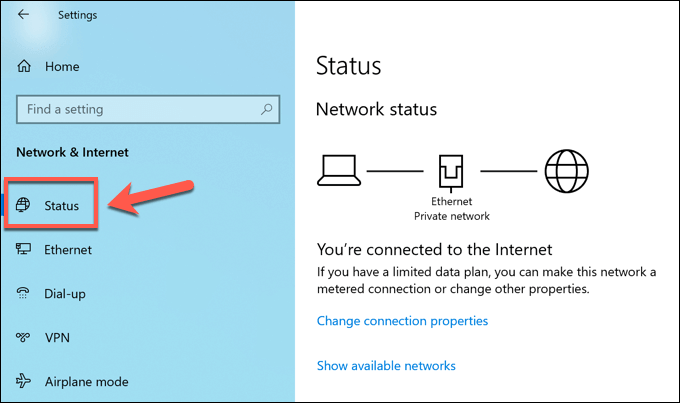
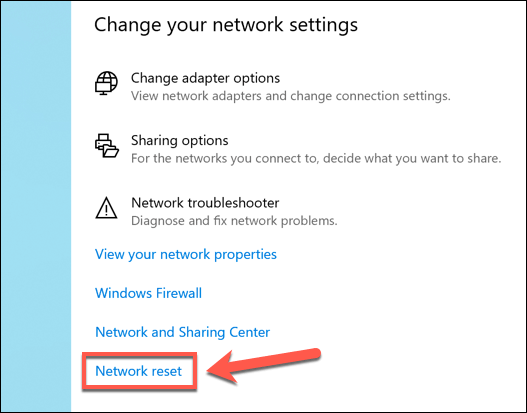
In the Windows Settings window, press Network & Internet > Status.
Click the Network Reset option in the Status menu to begin the network reset process.
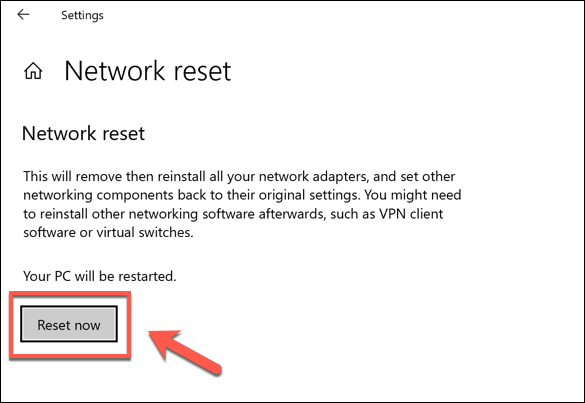
In the Network Reset menu, an explanation of the process will appear, explaining that Windows will reset your devices and network configuration. Press Reset now to begin resetting your devices.
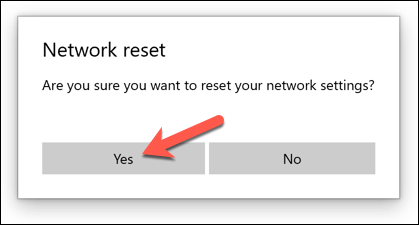
In the pop-up Network Reset box, press Yes to confirm and begin the process.
Windows will begin resetting your network devices and configuration at this point. Once this is complete, your PC will restart to ensure that your adapters are fully reset and ready to use again afterwards.
Using Windows PowerShell to Run Advanced Network Settings Tools
A full network reset using the Windows Settings tool will wipe the slate clean and should reset your adapters and connections to a default configuration. You can tweak your settings further, or reset other parts of your configuration should you need to, by using the Windows PowerShell.
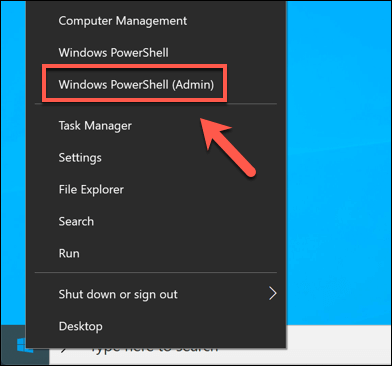
To launch a PowerShell terminal window with administrative access, right-click the Windows Start menu and press Windows PowerShell (Admin).
There are several network commands that can be launched in a PowerShell window to fix or reset your network devices and settings. These include:
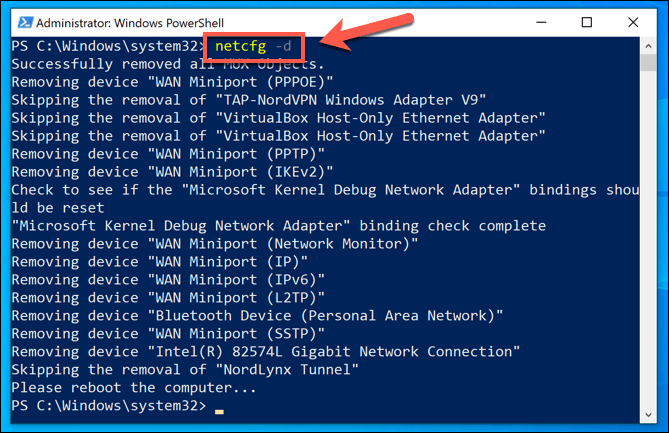
Clear-DnsClientCache – this will reset your current DNS cache.Get-NetAdapter – this will show a list of available network adapters on your device.Disable-NetAdapter -name “name” – this will disable a network adapter, replacing “name” with the name of your chosen adapter (found using Get-NetAdapter).Enable-NetAdapter -name “name” – this will enable a network adapter. This command can follow an issued Disable-NetAdapter command to restart a network device.ipconfig /release – this will release your current IP address.ipconfig /renew – this will renew your IP address after being released.netsh winsock reset – this will reset your PC’s Winsock settings (used to help apps and other services on a Windows PC communicate on a network).netsh int ip reset – this will reset your PC’s TCP/IP stack (the essential components used for Windows networking).netcfg -d – this will remove all current network devices and their active connections and configurations. This is a similar, last-resort option to the Windows Settings method listed for resetting your network configuration shown above, and will require a PC restart afterwards.
To run any of these commands, type them into the PowerShell window and hit enter. This will ensure that the information or action you’ve requested (such as disabling a network adapter or resetting your DNS cache) is performed. While only netcfg -d will typically require a restart, restarting your PC after running several commands sequentially can help to ensure that any changes made are successful.
Managing a Windows 10 Network
Most users will resolve common networking issues by using the network resetting tool in the Windows Settings menu. If you’re still having trouble with connectivity, you may find that the Windows Troubleshooter can help in the first instance, however. If the device is new, you may need to update the drivers to get it working first. You may find that using a VPN can cause networking conflicts on Windows PCs. If this is the case, removing and reinstalling the VPN service can solve the issue, but if all else fails, reset your network devices to clear any configuration or device conflicts in your network settings.