We will create a shell script using variables, the tar command and the date command to create a dated backup file of a directory, with its subdirectories. A shell script is essentially a file containing a list of commands that are run in sequence. If you have a series of commands you regularly run in order, it is helpful to create a shell script containing these commands. Then, you only have to run the script file to run the commands.
Creating the Shell Script File
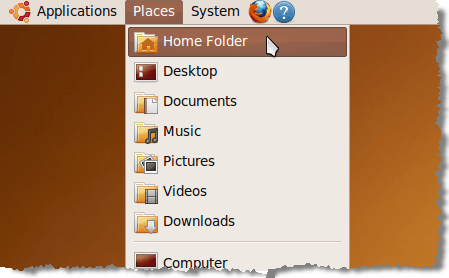
For this example, we are going to create a shell script to backup a directory containing files for a user guide. We are using the Gnome environment in Ubuntu. First, access your home directory, by selecting Home Folder from the Places menu. The File Browser opens to your home directory.
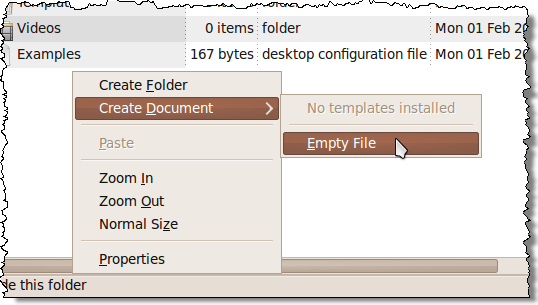
We are going to create a new empty file in which we will enter the commands for performing the backup. Right-click in the right pane and select Create Document | Empty File from the pop-up menu.
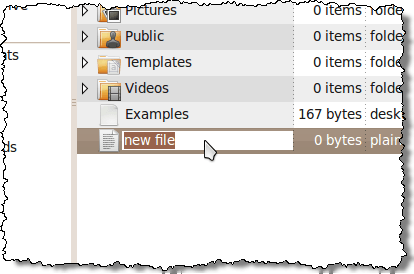
A file is added to the list and is ready to be renamed. Type in a name for the file, giving the file an extension of .sh.
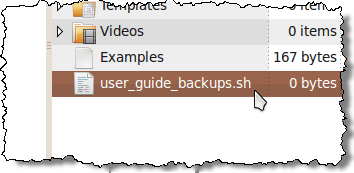
For this example, we named our file user_guide_backups.sh.
Now we need to add the commands to the file. Right-click on the name of the file and select Open with gedit from the pop-up menu.
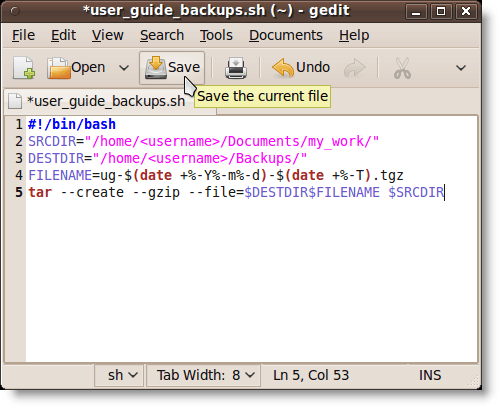
The file opens in gedit. Enter the following lines into the file and click Save. The purpose of each line is listed below.
NOTE: You can also copy the following text and paste it into gedit. Be sure to change
Line-by-Line Description
The following table describes what each line is in the shell script file.
Editing the Permissions on the Shell Script File
Before running your script, you need to make sure the file has the correct permissions. To do this, open your Home Folder again as mentioned above and right-click on the shell script file. Select Properties from the pop-up menu.
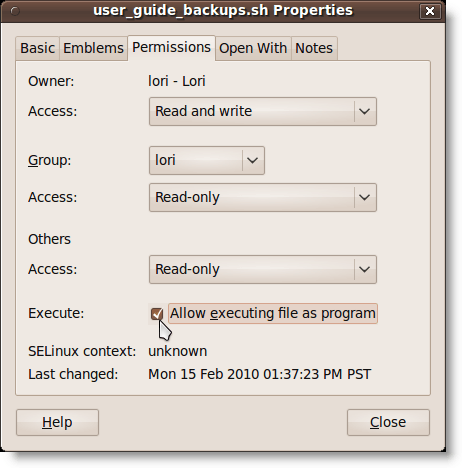
The Properties dialog box displays. Make sure the Execute check box is selected.
Click Close.
Running the Shell Script
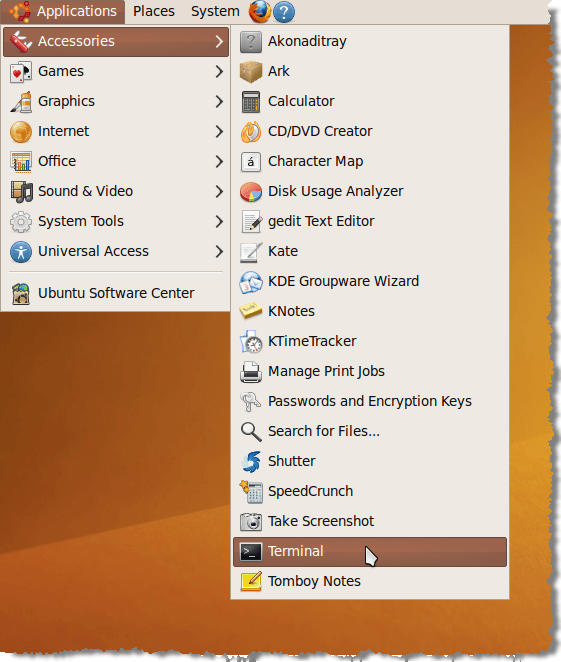
To run the shell script, open a terminal window by selecting Accessories | Terminal from the Applications menu.
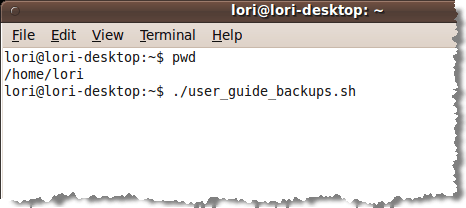
When the Terminal window opens, you should be in your Home Folder by default. Typing pwd on the command line and pressing enter confirms this fact. At the prompt, type ./user_guide_backups.sh and press Enter.
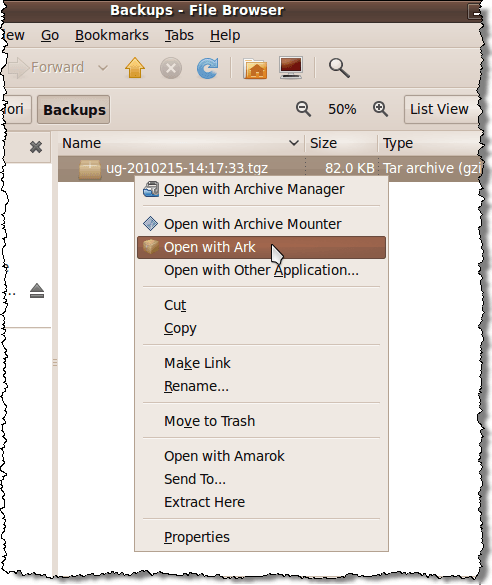
You should have a .tgz file in the Backups folder in your Home Folder. If you right-click on the filename, you see several options for opening the archive in one of the available archiving programs, or extracting the files directly to the Backups folder using the Extract Here command.
More information
The links below provide more information about shell scripts, the tar and date commands, and other Linux commands.
Scripting
A quick guide to writing scripts using the bash shell Bash Shell Scripting – 10 Seconds Guide | All about Linux Bash Reference Manual
Linux Commands
tar MAN Page date MAN Page bash commands – Linux MAN Pages Exploring these pages will help you to construct your own useful bash shell scripts.