If you use a Windows 11 PC, you have multiple ways to perform a system reboot. Although you probably won’t need them all, it’s always better to know about alternative methods should the situation arise.
1. Restart Windows 11 via Start Menu
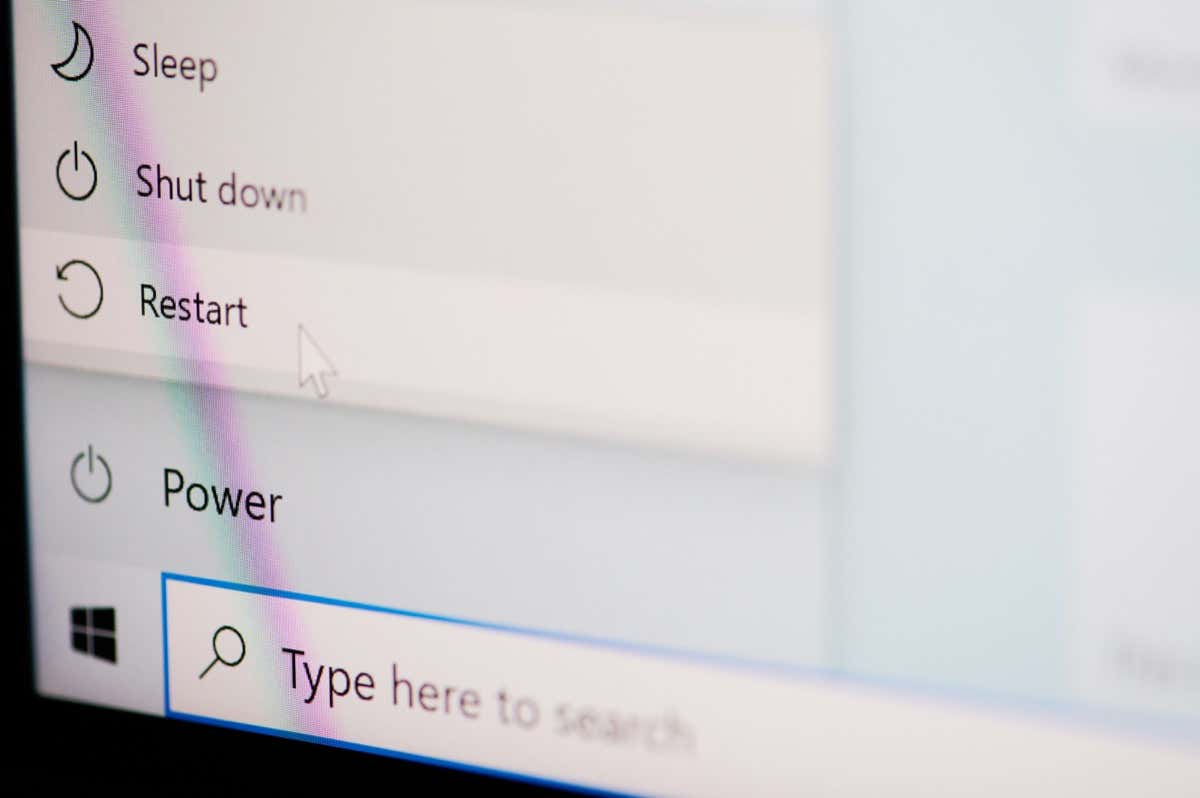
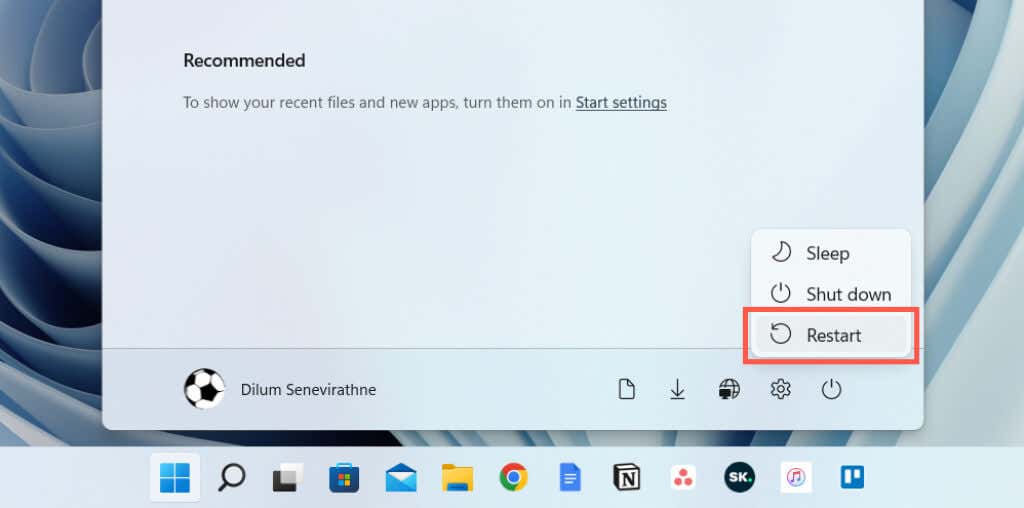
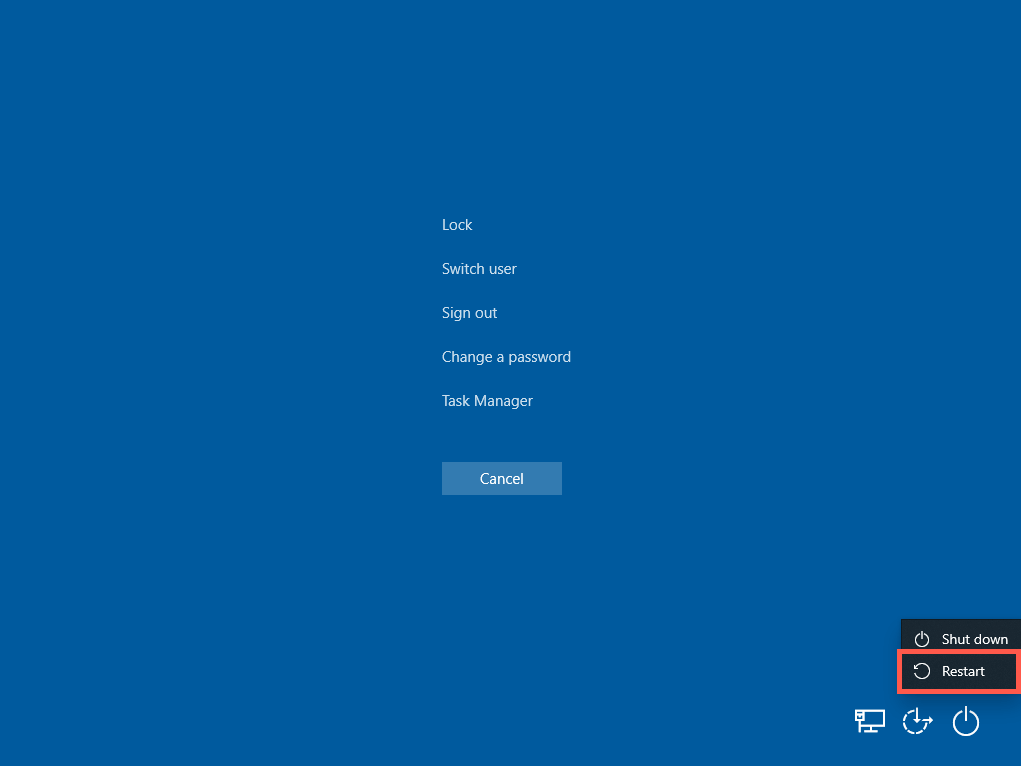
The most straightforward way to restart a Windows 11 PC is through the Start menu—simply select the Power icon on the right corner and choose Restart. If you’re restarting your computer after installing an update from Microsoft, you’ll see an additional Update and restart option and a time estimate. Select it if you want to complete the update.
2. Restart Windows 11 via Power User Menu
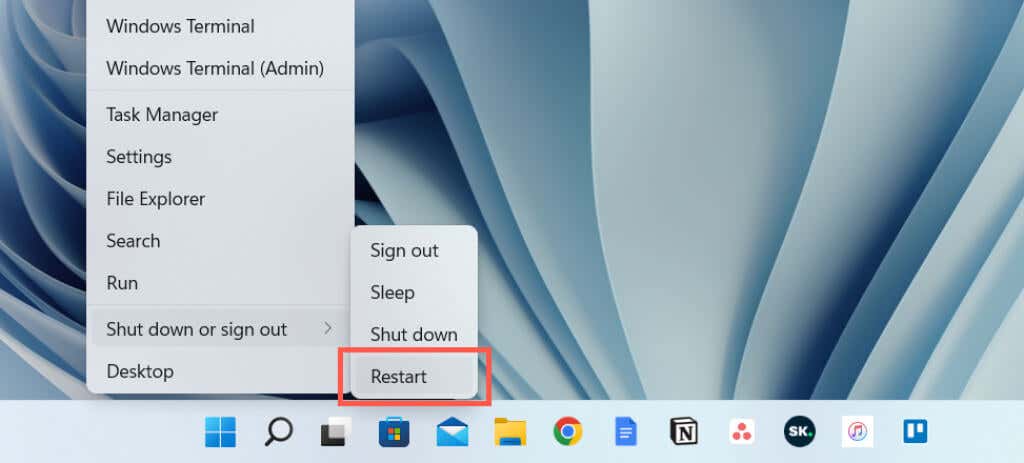
One more quick way to restart your computer is to use the Power User Menu. Right-click the Start button on the taskbar (or press Windows + X), point to Shut down or sign out, and select Restart.
3. Restart Windows 11 via Keyboard Shortcut
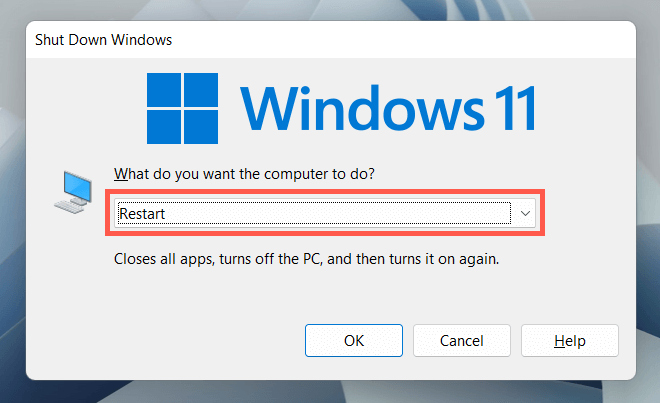
You can also restart your computer with the help of a keyboard shortcut. Just visit your desktop and press Alt + F4 (or Fn + Alt + F4 if the keyboard has a Function key). On the “Shut Down Windows” dialog pop-up that appears, choose the Restart power option on the drop-down menu and select OK.
4. Restart Windows 11 via Ctrl-Alt-Del Screen
Another way to restart your PC is through the Ctrl + Alt + Del screen (a.k.a. the Windows Security screen) in Windows 11. Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete, select the Power icon at the bottom right corner of the screen, and select Restart. The Ctrl + Alt + Del screen is accessible even when your system freezes, making it an ideal way to restart a stuck PC. It even provides immediate access to the Task Manager, so you may want to end any stuck processes before you resort to a system reboot.
5. Restart Windows 11 via Lock/Login Screen
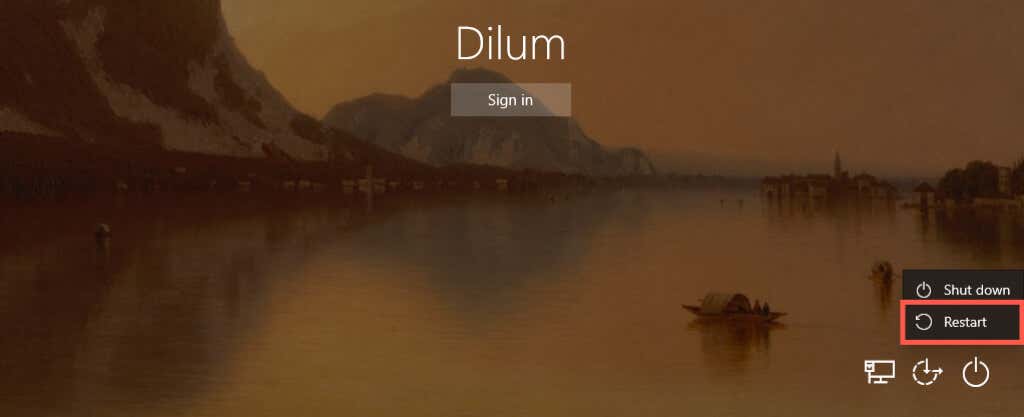
You don’t have to be logged into your user account to reboot your PC. If you’re at the Login or Lock Screen and want to restart Windows 11 for some reason, select the Power icon on the lower right corner and choose Restart.
6. Restart Windows 11 via Command Line
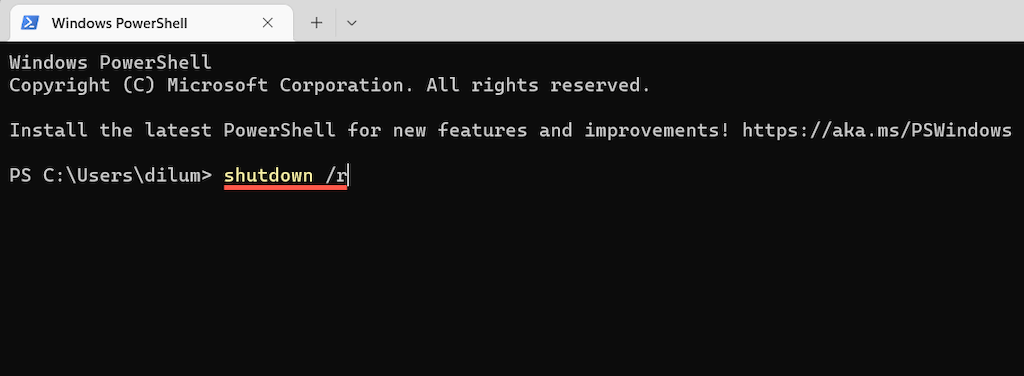
If you’re an aspiring terminal geek, you can restart your Windows 11 PC via the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell console. Start by opening Command Prompt (search for cmd.exe on the Start menu) or Windows PowerShell (select Windows Terminal on the Power User Menu). Then, type shutdown /r and press Enter. Your computer will reboot in 60 seconds. If you want your computer to restart immediately, run the command with additional switches: shutdown /r /t 0 Feel free to change the numerical value in the command above to determine how long the operating system takes to reboot itself in seconds—e.g., 3600 if you want to delay the restart by one hour.
7. Restart Windows 11 via Run Box
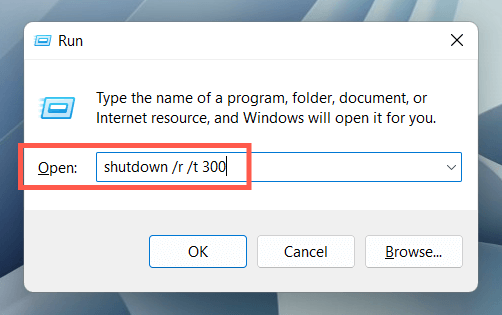
It’s also possible to execute the commands above using Run. Press Windows Key + R to open a Run box, type shutdown /r (Windows 11 will restart in 60 seconds) or shutdown /r /t time_in_seconds (if you want to perform an immediate or delayed reboot), and press Enter.
8. Hard Reboot Windows 11
If your computer is completely frozen and none of the methods above help, a hard reboot is on the cards. It could lead to file corruption and data loss, so we don’t recommend it unless necessary.
To perform a hard reboot, simply press and hold the Power button (some laptops may require you to hold down an additional button) until the screen darkens. Then, press the Power button again to turn on your PC.
On desktop PCs, the CPU casing may sport a dedicated Restart button; if yours does, use that to hard reboot your computer.
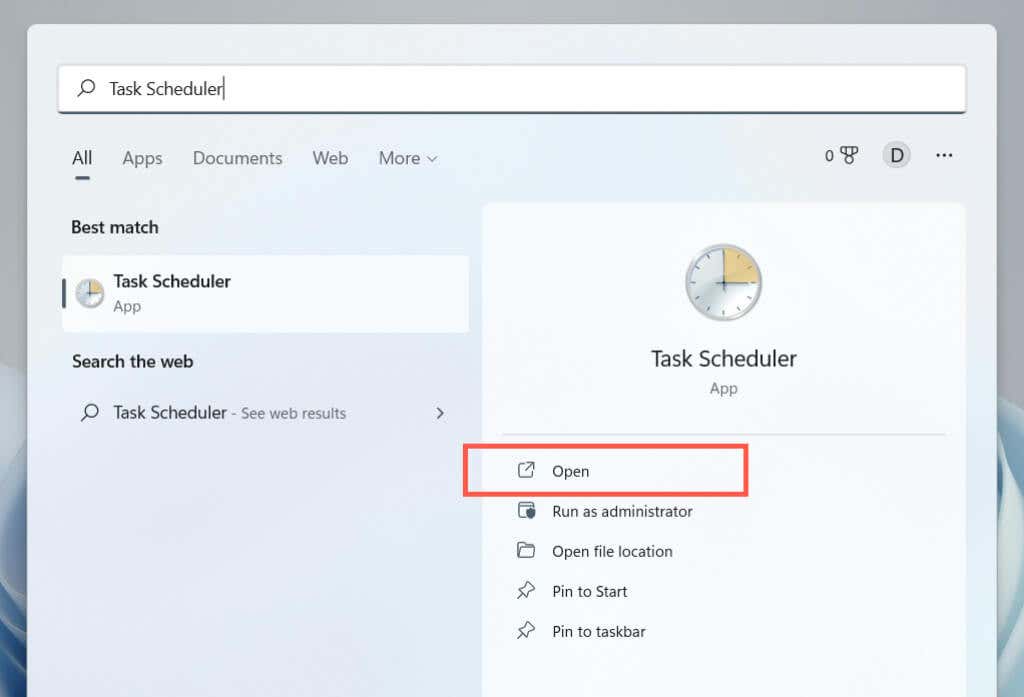
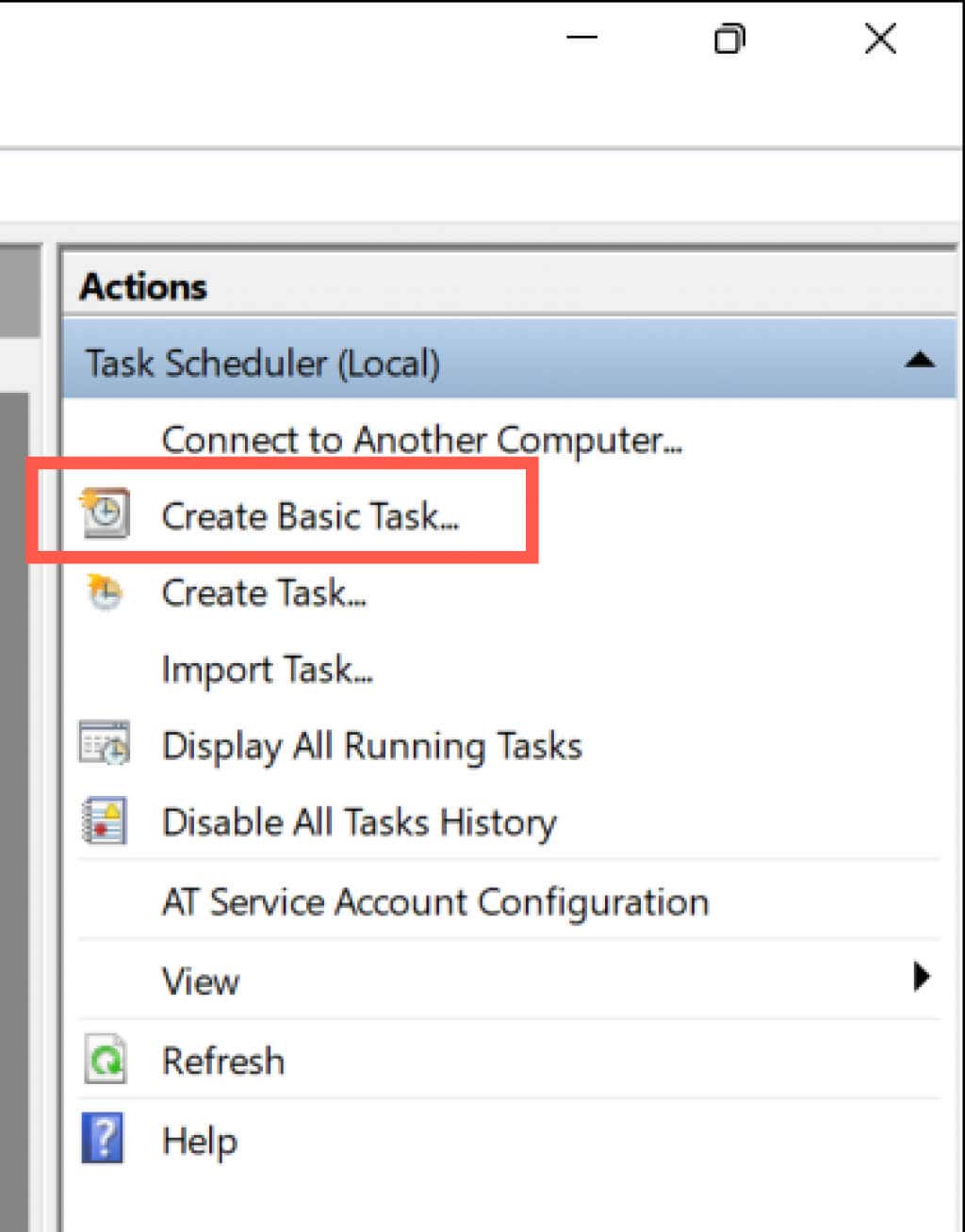
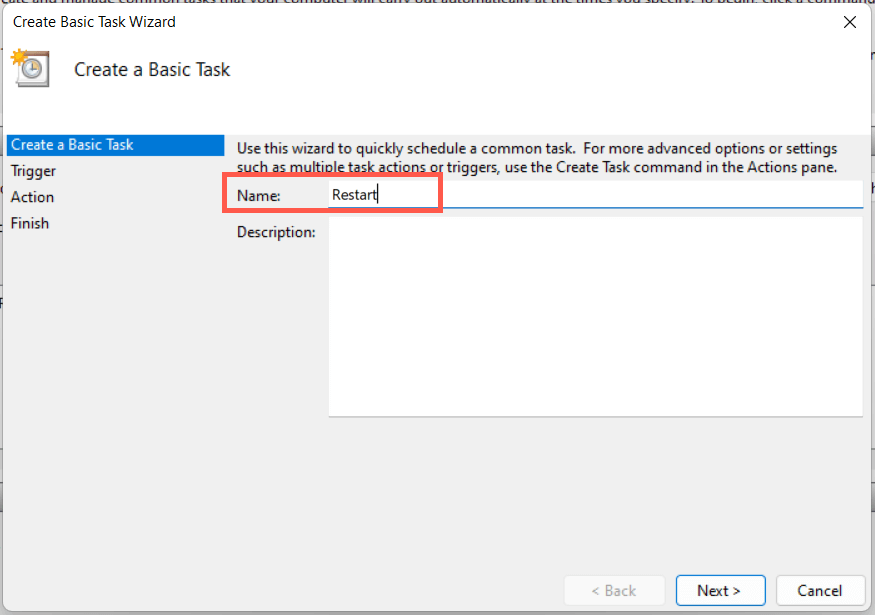
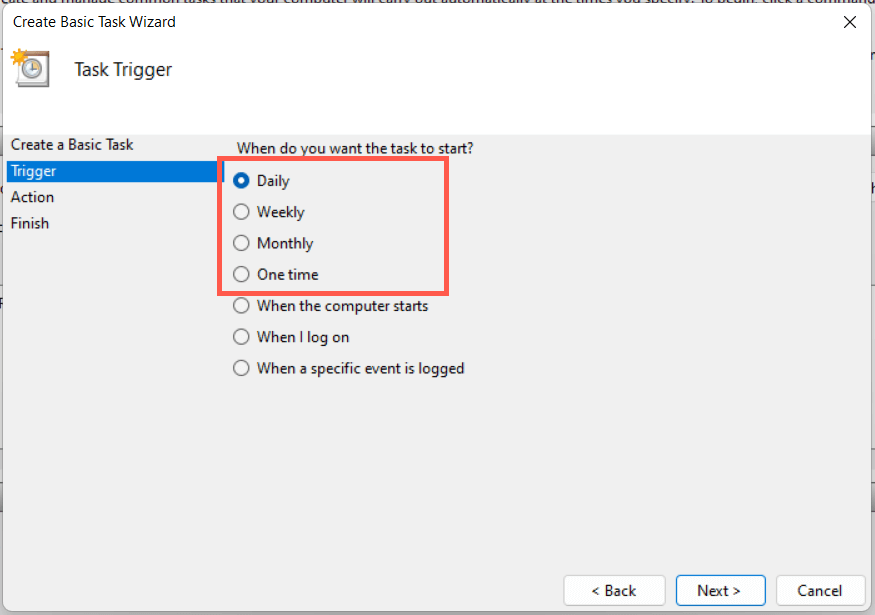
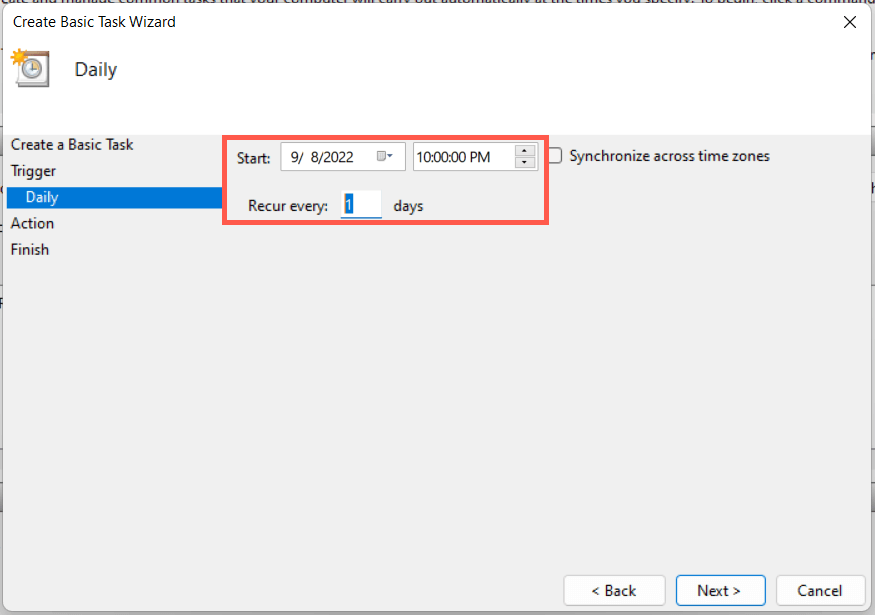
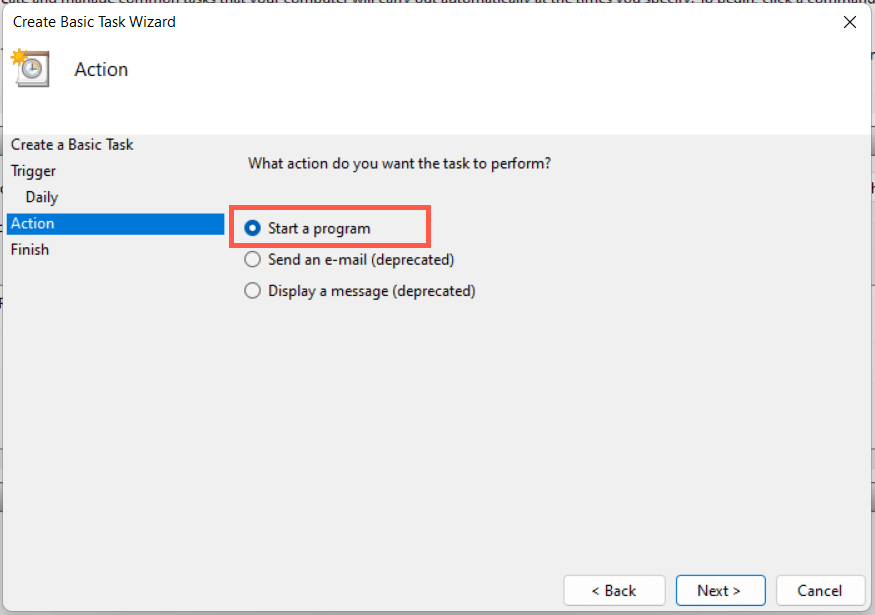
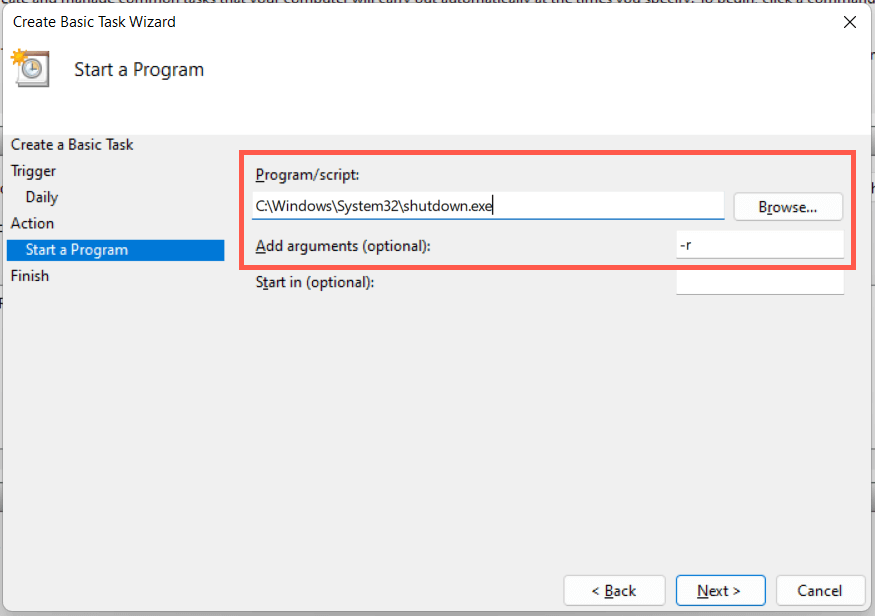
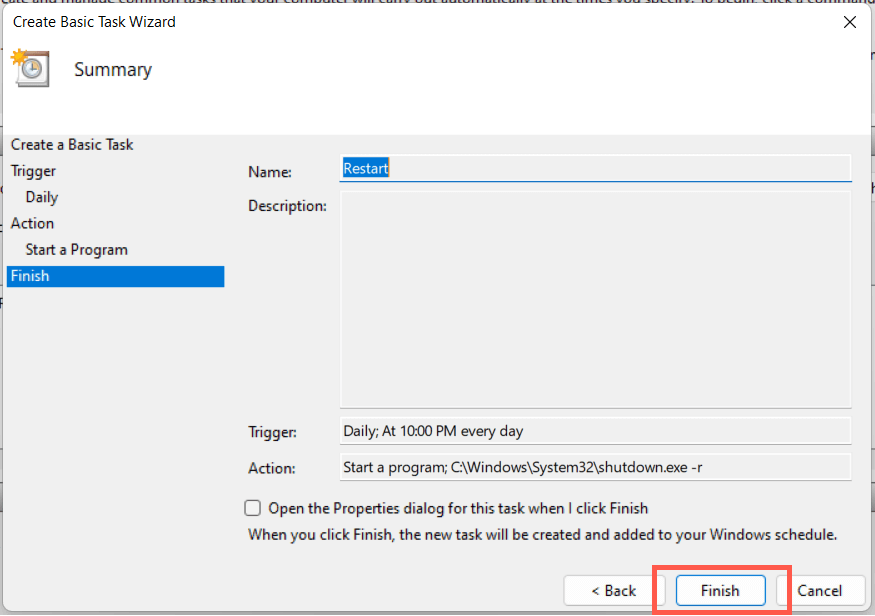
9. Schedule a Windows 11 Restart
It’s possible to schedule a restart using the Task Scheduler built into Windows. You also have the option of making that a one-off or recurring task. To do that: C:\Windows\System32\shutdown.exe You have 60 seconds until your system reboots when the task begins running. Add the -t time-in-seconds switch in step 8 if you want to adjust the delay duration.
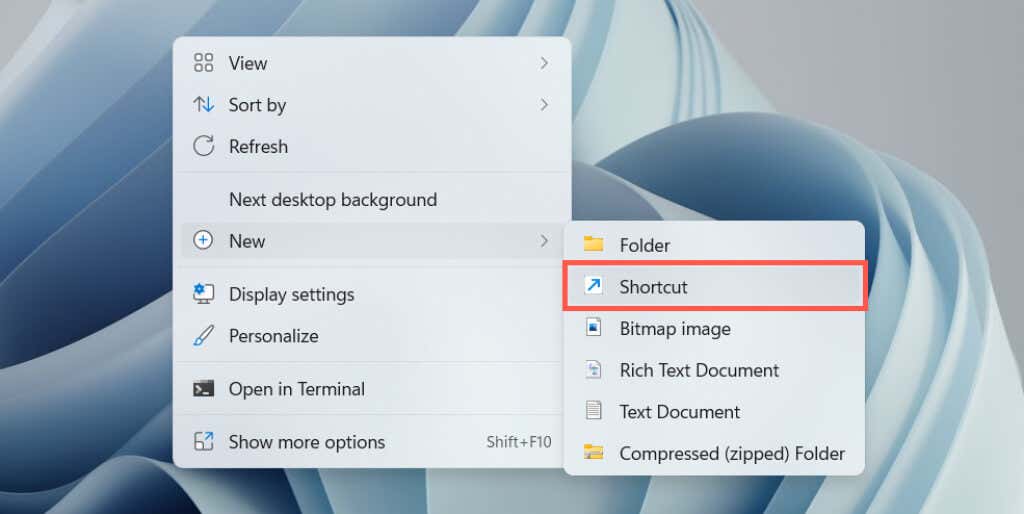
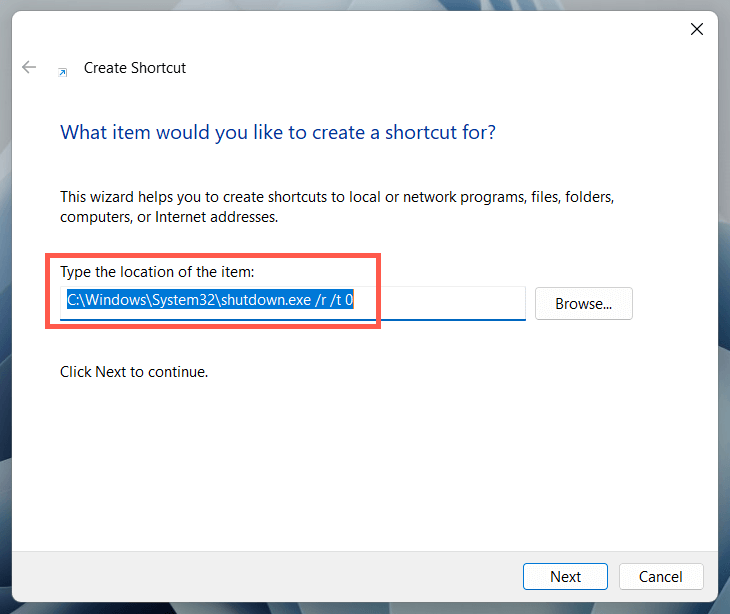
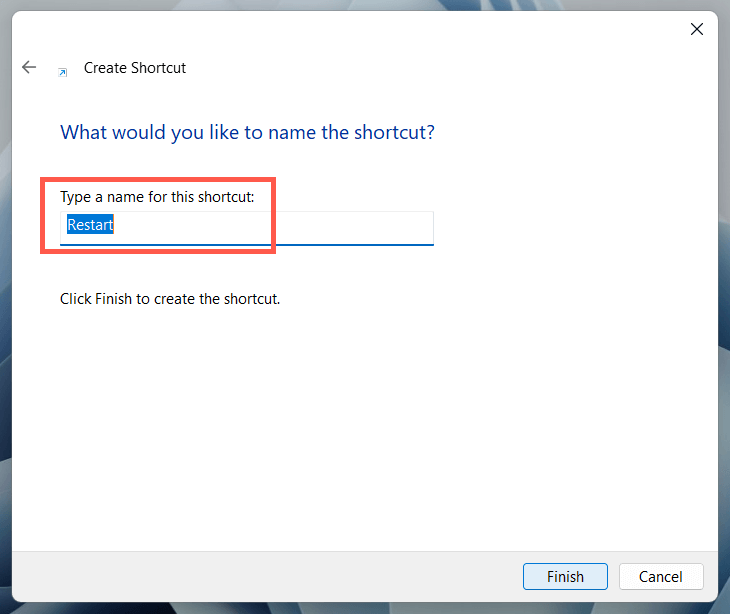
10. Restart Windows 11 via Desktop Shortcut
If you want a super-fast way to restart Windows, you always have the option of creating a desktop shortcut! To do that:
Shutdown vs. Restart: What’s the Difference?
Before we wrap up, it’s best to point out the difference between manually powering down your PC and then turning it back on versus instructing the system to reboot on its own. Although both actions appear to accomplish the same thing, that’s not the case due to a feature called Fast Startup.
When you select Shutdown (available as an option in many of the above methods), Fast Startup caches various forms of system data, allowing your computer to boot faster from a cold start. However, that can cause issues while troubleshooting persistent problems with the operating system.
Fast Startup does not kick in if you pick Restart, making it the better option if you intend to fix issues. It’s also the most convenient unless you don’t plan on turning on your PC anytime soon.
Nevertheless, you do have the option of disabling Fast Startup if you want. Open the Windows Control Panel, go to Hardware and Sound > Power > Choose what the power buttons do, and uncheck the box next to Turn on fast startup (recommended).